Commence your cyber security resilience journey with the ACSC Essential eight, the ACSC is short for the Australian Cyber Security Centre and the ACSC the central source for all things related to the Australian Government cyber security strategy.
The ACSC is not the sole source of truth and most of the ACSC recommendations do relate back to international standards bodies such as NIST CSF, therefore following the recommendations of the Essential 8 will reduce your risk of cyber attack dramatically when compared to your competitors who do not undertake any risk reduction strategies.
Time and time again we are being inundated with advertising and “cold” calls from sales people informing us that we must have cyber security. Statements such as “your competitors are being breached, you will be next”, or “99% of small businesses in Australia were breached last year costing them a combined $1 trillion” (this last “fact” was made up!).
Where to start
In a world full of choice available, where does a business start their Cyber Security Strategy? Let us first change the term from cyber security to cyber resilience because what is needed is resilience not security, there is no strategy that will give a business a 100% risk reduction guarantee.

Your business must have Cyber resilience planning and processes in place, what these plans and processes are will vary depending on what proportion of your business relies on Information Technology, how you work and what you do for business.
- 1. A mechanics workshop with a 3-4 PC’s running diagnostics and invoicing / account software may need a very simple plan that involves: Training, regular backups and contact number and details of their IT provider incase of a cyber incident.
2. A business consultancy with 20 PCs/laptops and mobile devices that rely 37.5 hours a week on their client data being available may need a much more descriptive process to manage their cyber resilience. Their cyber resilience plan may include: Training, Email security, web security, detection response services, recovery planning, incident recovery plans and communications plan as well as 24/7 contact details of their IT support provider.
3. Any larger organisation or any organisation that relies heavily on their Online services, data or applications must have a full cyber resilience plan, otherwise they are risking their livelihoods, and the livelihood of all of their staff members in the event of a cyber incident causing the business to fail.
How to build cyber resilience?
- Critical: First identify whether you have someone in your business who understands technology and wants to take on the responsibility of managing cyber resilience for your business, this is necessary/critical.
- If there is no one on staff then engage your trusted IT provider and work with them to have coverage for cyber resilience planning.
A Managed Service Provider (MSP) or Managed Security Services Provider (MSSP) can assist in planning, though listen to how they understand and relate back to you about your plans – if they try to address problems that you do not have then you may not have the right MSSP for your requirements. Ask questions, like an annoying 8 year old, “why?” and if the answer does not sound authentic then do not accept.
In cyber security there are many ways to lose a lot of money and not have a positive result, or any outcome for the investment spent – except lost money.

Planning – ACSC essential 8 Mitigation Strategy
The ACSC essential 8 is a good place to commence your planning you have limited experience, the ASD 8 control functions are fairly basic, yet capable of providing a good baseline of security for your business.
https://www.cyber.gov.au/acsc/view-all-content/essential-eight
The 8 controls are below, these are level one and the baseline for your cyber resilience planning :
Description (maturity level 1)
Application control
- The execution of executables, software libraries, scripts, installers, compiled HTML, HTML applications and control panel applets is prevented on workstations from within standard user profiles and temporary folders used by the operating system, web browsers and email clients.
Much of application control at level 1 is managed by the operating system you are using. Modern browsers do a very good job (though not perfect) of sandboxing activities. The more that your business is able to run using Software as a Service (web browser based) the safer you are. Microsoft Group policies can also help manage this.
Patch applications
- Patches, updates or vendor mitigations for security vulnerabilities in internet-facing services are applied within two weeks of release, or within 48 hours if an exploit exists.
- Patches, updates or vendor mitigations for security vulnerabilities in office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products are applied within one month of release.
- A vulnerability scanner is used at least daily to identify missing patches or updates for security vulnerabilities in internet-facing services.
- A vulnerability scanner is used at least fortnightly to identify missing patches or updates for security vulnerabilities in office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products.
- Internet-facing services, office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, Adobe Flash Player, and security products that are no longer supported by vendors are removed.
Modern operating systems are configured to check for updates regularly. Web apps are other platforms (Assets) should be inventoried as a part of your cyber resilience plans, the assets criticality, the backup and recovery plan, along with current application version and the person responsible for managing the platform. All applications should be configured to auto update if connected to a network. Staggering the update schedule can assist in ensuring that if an update breaks something that not all users are affected at once. For vulnerability scanning determine whether you need full detection and response services or just anti virus on all your systems. Microsoft Defender may be suitable or another more feature rich platform, if you run multiple Operating systems then try and select a product that covers all platforms for simplification of management. Hint: if no one is responsible then you are responsible until you can find another.
Configure Microsoft Office macro settings
- Microsoft Office macros are disabled for users that do not have a demonstrated business requirement.
- Microsoft Office macros in files originating from the internet are blocked.
- Microsoft Office macro antivirus scanning is enabled.
- Microsoft Office macro security settings cannot be changed by users.
If you are running a Microsoft Active directory then controlling macros is relatively easy to do centrally through Microsoft Active Directory Group Policy Objects . If you are not running AD but are an Microsoft Office 365 subscriber then it is also fairly easy to prevent macros from running if the document came from the internet. For most users there is no reason to be running macros on their workstations.
User application hardening
- Web browsers do not process Java from the internet.
- Web browsers do not process web advertisements from the internet.
- Internet Explorer 11 does not process content from the internet.
- Web browser security settings cannot be changed by users.
Active Directory Group Policy, Firewall rules.
Restrict administrative privileges
- Requests for privileged access to systems and applications are validated when first requested.
- Privileged accounts (excluding privileged service accounts) are prevented from accessing the internet, email and web services.
- Privileged users use separate privileged and unprivileged operating environments.
- Unprivileged accounts cannot logon to privileged operating environments.
- Privileged accounts (excluding local administrator accounts) cannot logon to unprivileged operating environments.
Least privilege access is built into modern operating systems, users should not need admin access to their workstations for normal use. If the devices they use are BYOD then the mechanism they use to access corporate applications must be managed so that malware can not cause an issue to perpetuate. This can be achieved with solutions like Microsoft Terminal services, Remote Desktop or Citrix to isolate the end users device from the corporate network through a remote session.
Patch operating systems
- Patches, updates or vendor mitigations for security vulnerabilities in operating systems of internet-facing services are applied within two weeks of release, or within 48 hours if an exploit exists.
- Patches, updates or vendor mitigations for security vulnerabilities in operating systems of workstations, servers and network devices are applied within one month of release.
- A vulnerability scanner is used at least daily to identify missing patches for security vulnerabilities in operating systems of internet-facing services.
- A vulnerability scanner is used at least fortnightly to identify missing patches for security vulnerabilities in operating systems of workstations, servers and network devices.
- Operating systems that are no longer supported by vendors are replaced.
Copied from above: Modern operating systems are configured to check for updates regularly. Web apps are other platforms (Assets) should be inventoried as a part of your cyber resilience plans, the assets criticality, the backup and recovery plan, along with current application version and the person responsible for managing the platform. All applications should be configured to auto update if connected to a network. Staggering the update schedule can assist in ensuring that if an update breaks something that not all users are affected at once. For vulnerability scanning determine whether you need full detection and response services or just anti virus on all your systems. Microsoft Defender may be suitable or another more feature rich platform, if you run multiple Operating systems then try and select a product that covers all platforms for simplification of management. Hint: if no one is responsible then you are responsible until you can find another.
Multi-factor authentication
- Multi-factor authentication is used by an organisation’s users if they authenticate to their organisation’s internet-facing services.
- Multi-factor authentication is used by an organisation’s users if they authenticate to third-party internet-facing services that process, store or communicate their organisation’s sensitive data.
- Multi-factor authentication (where available) is used by an organisation’s users if they authenticate to third-party internet-facing services that process, store or communicate their organisation’s non-sensitive data.
- Multi-factor authentication is enabled by default for non-organisational users (but users can choose to opt out) if they authenticate to an organisation’s internet-facing services.
Many vendors and Microsoft can provide MFA solutions, MFA solutions will not only help with your users connecting to critical systems, it will also help with trusted partners and home workers connecting to your business. ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ Five stars..... If you do this then you are a rock star. The single most critical control function for an organisation is having multi-factor authentication where ever possible. Yes, even SMS! though it is not as secure as App based it is likely to be much better than your competitors are doing now and makes it much more difficult for a cyber criminal to infiltrate your organisation.
Regular backups
- Backups of important data, software and configuration settings are performed and retained in a coordinated and resilient manner in accordance with business continuity requirements.
- Restoration of systems, software and important data from backups is tested in a coordinated manner as part of disaster recovery exercises.
- Unprivileged accounts can only access their own backups.
- Unprivileged accounts are prevented from modifying or deleting backups.
Backups are a critical control function, if you have reliable backups then you can recover and continue business in the event of a failure or a cyber attack (malware for example). As a part of your Planning process, the Assets that were identified will make up your backup routine and frequency. A platform that does not change much may only need to be backed up once a week, whereas your critical systems may need to be backed up daily. NOTE: Pay careful attention to your SaaS applications and what the Service level agreement(SLA) is for availability, recovery and costs etc.
In summary
There is very little software outlay cost in the above ASD 8 control functions, if you wish to spend more capital then you will benefit from improved management and functionality, but it is easy to improve your cyber resilience today.
Microsoft provide a mapping between M365 Business premium licenses and the Essential 8 mitigations to help provide customers with some guidance:
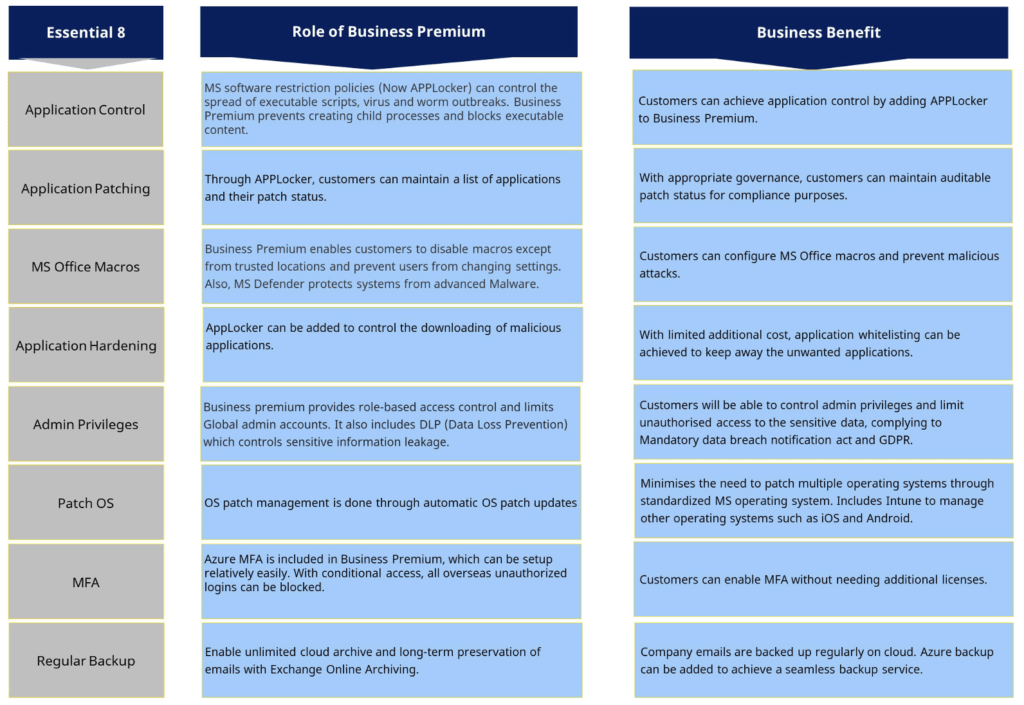
Implementing best practise controls on your workstations will limit the attacks your business is likely to face now and in the future, your goal is to never be at the back of the herd.
Being the fastest and strongest member in the herd is not necessary, just do not become the weakest, your perimeter is being scanned every day (at home and in the office) by cyber criminals.
Within your organisation boundaries your staff make mistakes by clicking Malware links they should not click every day, (20% of staff will click on a malware link) so be prepared to handle this by having a plan and securing your IT systems.

Part #2: training your people (coming soon)
Contact us if you would like to know more and how we can help you achieve better cyber resilience






Leave a Reply